DRO-InstructZero: Distributionally Robust Bayesian Optimization for Large Language Models
ICLR, 2026 (under review)
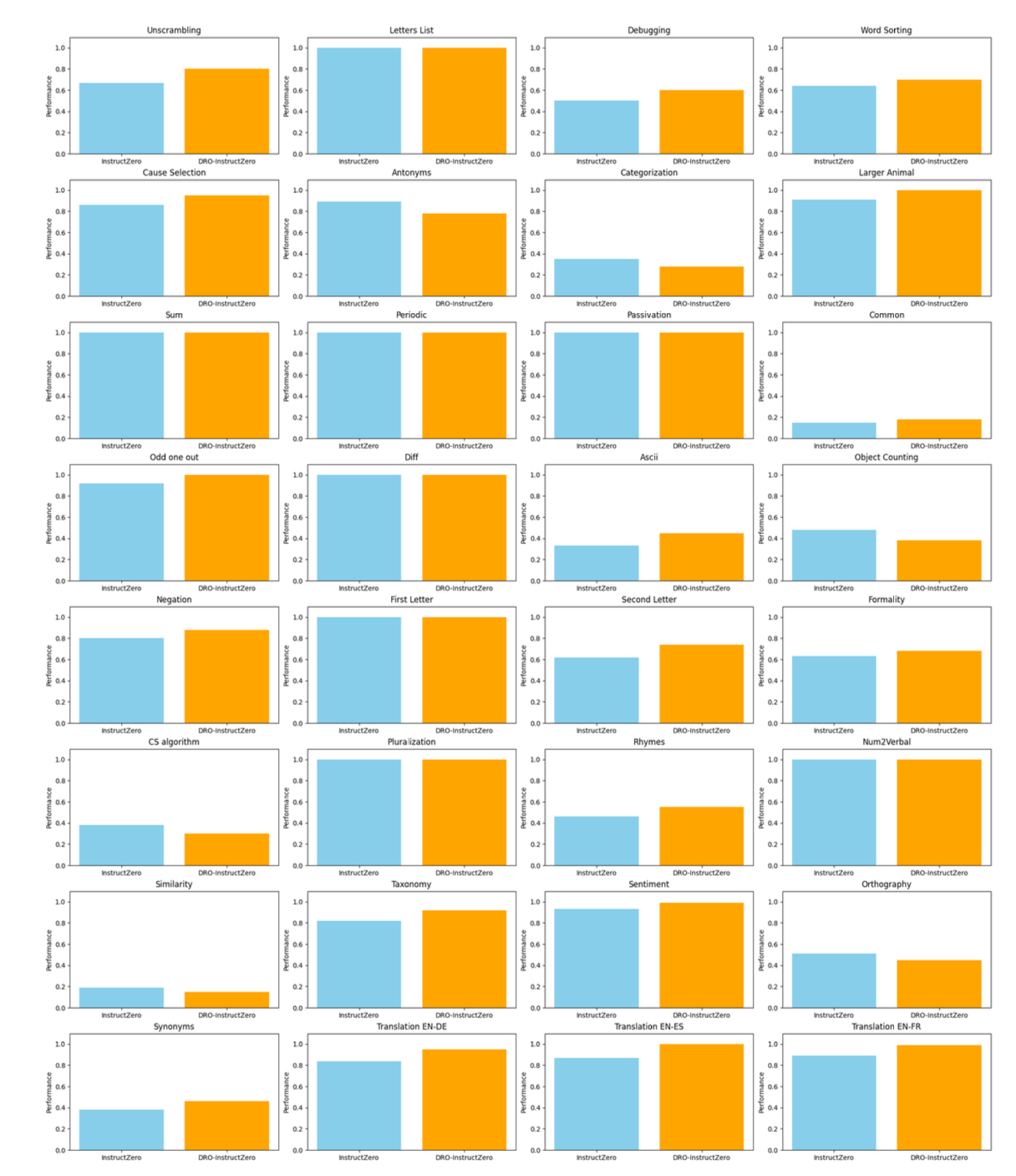
Large language models are highly sensitive to prompt wording. However, popular automatic prompt search methods, including InstructZero, often degrade under distribution shift and adversarial evaluation because they optimize expected performance under a single evaluation distribution. Consequently, prompts that work in one setting frequently fail to transfer. To address this, DRO-InstructZero formulates zero-shot prompt optimization as robust Bayesian optimization. Specifically, an f-divergence ball defines an ambiguity set around the evaluation distribution, and a robust acquisition rule maximizes worst-case expected utility while retaining the query efficiency of Bayesian search. Therefore, the search explicitly targets reliability under distribution shift rather than average behavior alone. Experiments follow the instruction-induction protocol with matched query budgets across formality rewriting, code debugging, and translation. For example, on BIG-Bench informative-to-formal rewriting, accuracy improves from 61.3 ± 0.7% to approximately 85–90%, yielding an absolute gain of about 25–30 points. Moreover, auto-debugging shows about +25-point gains under domain shift. Meanwhile, stable tasks such as cause-and-effect remain above 96%, indicating no loss on in-distribution cases. Furthermore, improvements are consistent across divergence choices and decoding temperatures. Overall, DRO-InstructZero connects distributionally robust optimization with prompt learning, offering a plug-and-play and general approach for reliable, transferable prompt alignment under real-world uncertainty.